Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that plays a crucial role in supporting the body’s structure and facilitating movement. It is found in various parts of the body, including the nose, ears, ribs, and joints.
It is made up of cells called chondrocytes, which are embedded in a matrix of collagen fibers and proteoglycans. The collagen fibers provide tensile strength, while the proteoglycans absorb water, giving the tissue compressive strength.
There are three types of cartilage: hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage is the most common type and is found in the joints, the rib cage, and the trachea. Fibrocartilage is found in areas that require extra support, such as the intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis. Elastic cartilage is found in areas that need flexibility, such as the ears and the epiglottis.
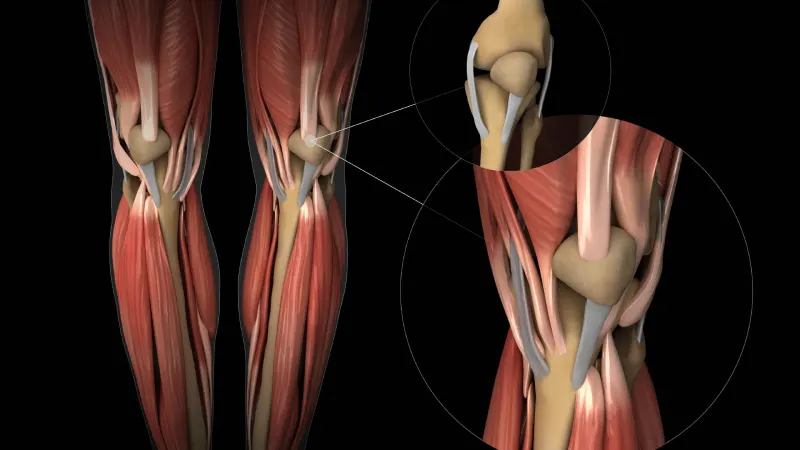
One of the key functions of cartilage is to cushion and protect the joints.
The smooth surface of the hyaline cartilage in the joints allows for frictionless movement, and it acts as a shock absorber, preventing damage to the bones. When it is damaged or worn away, it can lead to pain, stiffness, and eventually osteoarthritis.
It has a limited ability to repair itself due to its avascular nature (lack of blood vessels), but there are some treatments that can help. In some cases, small pieces of it can be transplanted from a healthy part of the joint to the damaged area. In other cases, stem cells or growth factors can be used to promote the growth of new cartilage.
Aside from its role in joints, it also plays a vital role in other parts of the body. For example, the elastic in the ears helps to direct sound waves towards the eardrum, while the hyaline cartilage in the trachea helps to keep the airway open.
In conclusion, it is a fascinating and important tissue that plays a crucial role in supporting the body’s structure and facilitating movement. While it has limited regenerative abilities, new treatments are being developed to help repair damaged cartilage and improve joint health.
What are the different types of cartilage?
There are three main types of it: hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage. Hyaline is the most common type and is found in the joints, the rib cage, and the trachea. Fibrocartilage is found in areas that require extra support, such as the intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis. Elastic is found in areas that need flexibility, such as the ears and the epiglottis.
What is the function of cartilage?
It has several important functions in the body, including: Supporting the body's structure: It provides structural support to the body and helps to maintain the shape of certain organs and tissues. Facilitating movement: The smooth surface of it in the joints allows for frictionless movement, and the it acts as a shock absorber, preventing damage to the bones. Protecting organs: It helps to protect organs from damage by absorbing shock and distributing forces.